
Self-Employment Tax: A Must-Know for Every Independent Earner
Ever wondered why your hard-earned money seems to vanish faster than expected, even when business looks busy? The answer often lies in self-employment tax—a tax obligation that catches many freelancers, sole proprietors, and independent contractors off guard. In India, this is commonly known as self-employed income tax, and it applies directly to the profits you make from running your own show.
Unlike salaried employees who see tax deducted automatically, you handle everything yourself. deAsra supports and engages entrepreneurs through practical resources, including the dreamBIG podcast, to make these rules easier to navigate. For a solid starting point, explore this in-depth guide on accounting and taxation.
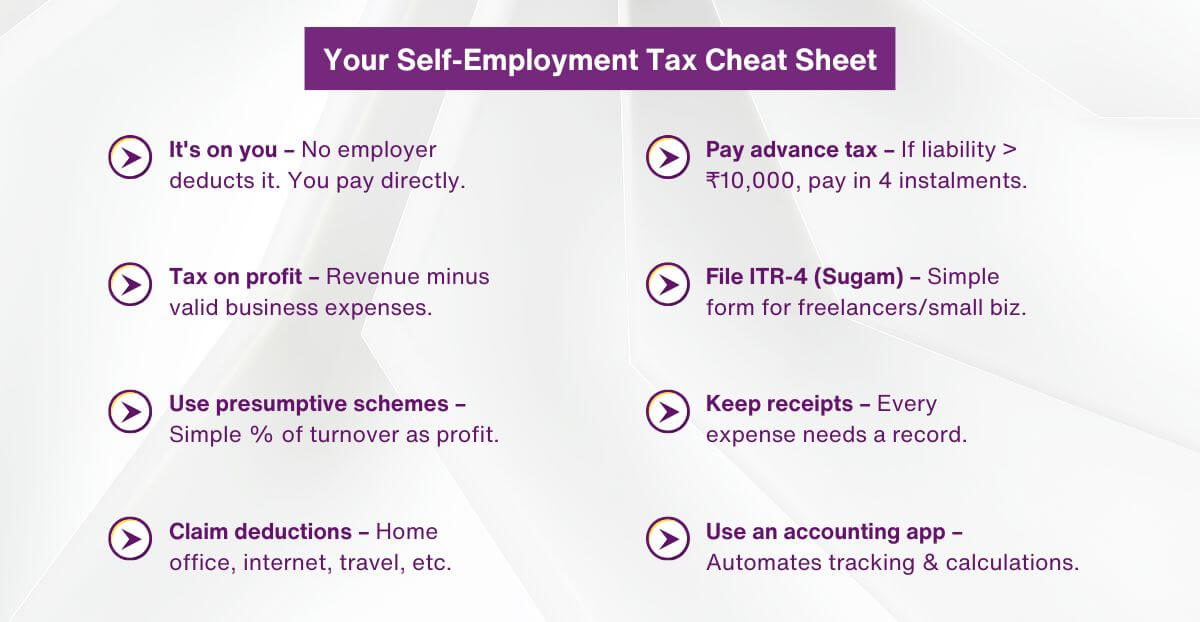
Self-employment tax is simply the income tax you pay on earnings from your business or profession. No boss withholds it for you. You calculate, pay advance instalments, and file returns on your own.
Why Self-Employment Tax Feels Different
Most people think of tax as something taken from salary slips. For the self-employed, it works differently. You pay self-employment tax on net profit after subtracting business expenses.
This covers freelancers, consultants, shop owners, doctors running clinics, and many more. If your yearly earnings cross ₹2.5 lakh, tax kicks in. The system pushes you to keep clear records. Good habits here save money and stress later.
Who Really Has to Pay It?
Anyone earning from independent work faces self-employment tax. That includes sole proprietors, freelancers, graphic designers, content creators, and small traders. Even partnerships pay it on each partner’s share.
Many choose presumptive schemes to keep things simple. Income below ₹2.5 lakh usually escapes tax. Still, track basic numbers for future reference. deAsra supports and engages business owners with checklists that spot liability quickly.
As Mr. Amit Lomte shared in the dreamBIG podcast, “accurate bookkeeping is the foundation for every business. From finances, such as loans, to compliance, everything is based solely on your books of accounts.”
Breaking Down the Tax Components
Start with gross receipts. Subtract genuine expenses—rent, travel, internet, raw materials—to reach net profit. Apply slab rates: 5% to 30% in the old regime, or simpler, lower rates in the new one.
Add 4% cess on top. Higher earners pay a surcharge too. GST may run alongside if your turnover qualifies. Input tax credit from GST often lowers the final self-employed income tax amount.
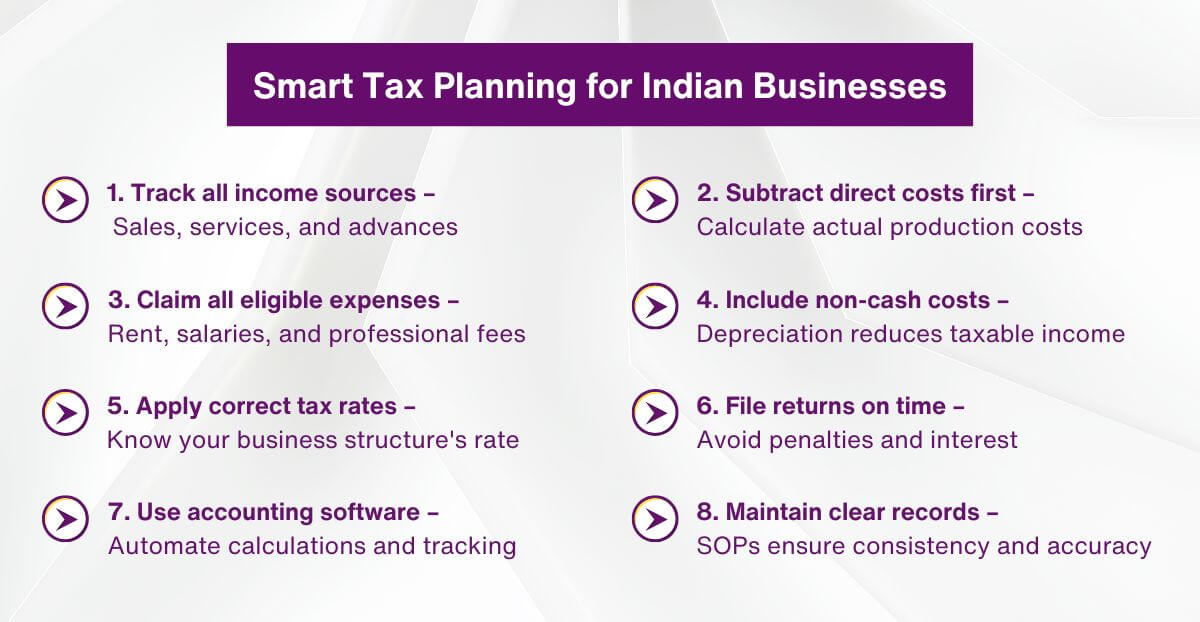
Simple Steps to Calculate Your Tax
Step one: Collect all income from the financial year.
Step two: list every allowable expense and deduct it. What remains is taxable profit. Apply the correct slab or presumptive percentage.
Under Section 44AD, many assume profit at 6% (digital payments) or 8% (cash) of turnover. This works up to ₹3 crore. If tax crosses ₹10,000, pay advance tax in four parts. Use tools to verify.
Mr. Anoop Tabe summed it up well in the dreamBIG podcast, “the true test of profitability lies in liquidity. Unless you have liquid money, it cannot be considered profit.”
The Easy Route: Presumptive Taxation
Section 44AD lets small businesses skip detailed books. Presume profit at 6% or 8%, depending on payment mode. Professionals use Section 44ADA and take 50% of receipts as profit.
This option suits doctors, lawyers, and engineers. Less paperwork means more time for actual work. Many growing ventures love this option. deAsra supports and engages users with examples showing when the scheme saves effort.
Smart Deductions to Cut Your Bill
Deduct office rent, phone bills, travel costs, and advertising. These lower taxable profits directly. Invest up to ₹1.5 lakh under Section 80C—PPF, ELSS, life insurance. Health premiums qualify, too.
Claim depreciation on laptops, furniture, and vehicles. Keep invoices safe. New regime trades deductions for lower rates. Pick what fits your spending pattern. Check deAsra’s practical guide on filing business taxes for deduction ideas that work.
Filing Your Return Without Panic
Use ITR-4 for presumptive taxation. Choose ITR-3 when you maintain full books. Enter data on the income tax portal. E-Verify within 30 days.
The normal due date for most is 31 July. Late filing allowed till December with fees. Collect bank statements, invoices, and TDS forms early. deAsra mentoring makes this step straightforward.
Common Traps to Dodge
Mixing personal groceries with business purchases inflates self-employed income tax. Skipping depreciation or advance tax adds avoidable interest. Under-reporting invites big penalties—sometimes 300% of the hidden amount.
GST mismatches cause notices. Reconcile monthly to stay clear. deAsra supports and engages businesses with SOPs that prevent these slip-ups.
Let Technology Do the Heavy Lifting
Apps like Vyapar, Zoho Books, or Tally pull bank entries automatically. They match GST data too. OCR turns phone photos of bills into entries. Reports appear in seconds.
These tools cut errors and free up your weekends. deAsra recommends beginner-friendly options for small setups. Technology turns tax work into a quick routine.
Wrapping It Up
Self-employment tax is part of being your own boss. Handle it right and it becomes a strength, not a burden. Stay organised, claim what you can, meet deadlines. You gain credibility with banks, clients, and partners.
deAsra supports and engages through dreamBIG and expert sessions with people like Mr. Amit Lomte and Mr. Anoop Tabe. Turn self-employment tax and self-employed income tax into tools that help your venture thrive.
FAQs
1. How is self-employment tax different from salary tax?
Self-employment tax applies to business profits with no automatic deduction. Salary tax uses TDS. You calculate and pay self-employed income tax yourself after expenses.
2. Does GST change my self-employment tax amount?
GST registration is separate but related. Credits from GST purchases often reduce your final self-employed income tax when claimed properly.
3. Can I switch tax regimes yearly?
Yes. Decide at filing time. The old regime gives more deductions. The new regime has lower rates but skips most claims. Choose yearly based on your numbers.
4. What records should I keep for self-employment tax?
Save invoices, receipts, bank statements, and expense proofs. Presumptive filers need less detail. Digital apps make storage simple and secure.
5. What if I forget the advance tax?
You pay 1% interest per month on the shortfall. It grows quickly. Plan early and pay on schedule to protect profits.

